On 2024-05-20, Pigsty v2.7 is released. The number of available extensions in this version reaches an astonishing 255, successfully elevating PostgreSQL’s versatility to a new height!
Additionally, we provide some new Docker app templates, including the open-source enterprise ERP suite — Odoo, Jupyter Notebook, and are the first to support Supabase GA version.
We’ve also paved the way for upcoming container versions, provided PolarDB support to help users pass domestic compliance audits, and officially differentiated Pro and Open Source editions.
Extensions Galore#
In “PostgreSQL is Eating the Database World,” I argued that PostgreSQL isn’t just a relational database — it’s a data management abstraction framework with the power to encompass everything and devour the entire database world.
What enables PG to do this, beyond being open source and advanced, is the real secret: extensions — extreme extensibility and a thriving extension ecosystem are PostgreSQL’s unique characteristics and the secret weapon that sets it apart from countless other databases.
Therefore, in Pigsty v2.7, we’ve re-examined the entire PostgreSQL ecosystem’s extensions and included some standouts:
| Extension | Version | Description |
|---|---|---|
| pg_jsonschema | 0.3.1 | JSON Schema validation |
| wrappers | 0.3.1 | Supabase’s foreign data wrapper bundle |
| duckdb_fdw | 1.1 | DuckDB foreign data wrapper (libduck 0.10.2) |
| pg_search | 0.7.0 | ParadeDB BM25 full-text search |
| pg_lakehouse | 0.7.0 | ParadeDB lakehouse analytics engine |
| pg_analytics | 0.6.1 | Accelerated analytics in PostgreSQL |
| pgmq | 1.5.2 | Lightweight message queue like AWS SQS/RSMQ |
| pg_tier | 0.0.3 | Tier cold data to AWS S3 |
| pg_vectorize | 0.15.0 | RAG vector search wrapper in PG |
| pg_later | 0.1.0 | Execute SQL now, get results later |
| pg_idkit | 0.2.3 | Generate various IDs: UUIDv6, ULID, KSUID |
| plprql | 0.1.0 | PRQL pipelined query language in PostgreSQL |
| pgsmcrypto | 0.1.0 | Chinese SM cryptography: SM2, SM3, SM4 |
| pg_tiktoken | 0.0.1 | Count OpenAI tokens |
| pgdd | 0.5.2 | Query database catalog via standard SQL |
| parquet_s3_fdw | 1.1.0 | Parquet FDW for S3/MinIO |
| plv8 | 3.2.2 | PL/JavaScript (V8) trusted language |
| md5hash | 1.0.1 | Native 128-bit MD5 data type |
| pg_tde | 1.0-alpha | Experimental encrypted storage engine |
| pg_dirtyread | 2.6 | Read dead tuples for dirty reads |
Many of these are extensions developed with Rust and pgrx, providing incredibly powerful capabilities:
Supabase’s wrappers looks like one extension, but it actually provides a Rust FDW framework with access to ten external data sources!
| FDW | Description | Read | Modify |
|---|---|---|---|
| HelloWorld | Demo FDW for basic FDW development | ||
| BigQuery | FDW for Google BigQuery | ✅ | ✅ |
| Clickhouse | FDW for ClickHouse | ✅ | ✅ |
| Stripe | FDW for Stripe API | ✅ | ✅ |
| Firebase | FDW for Google Firebase | ✅ | ❌ |
| Airtable | FDW for Airtable API | ✅ | ❌ |
| S3 | FDW for AWS S3 | ✅ | ❌ |
| Logflare | FDW for Logflare | ✅ | ❌ |
| Auth0 | FDW for Auth0 | ✅ | ❌ |
| SQL Server | FDW for Microsoft SQL Server | ✅ | ❌ |
| Redis | FDW for Redis | ✅ | ❌ |
| AWS Cognito | FDW for AWS Cognito | ✅ | ❌ |
This means you can now read and write BigQuery, ClickHouse, and Stripe data from PostgreSQL. Firebase, Airtable, S3, Logflare, Auth0, SQL Server, Redis, and Cognito also provide SQL read access through PostgreSQL.
The plprql extension provides a new SQL-like database query language called PRQL:
from invoices
filter invoice_date >= @1970-01-16
derive {
transaction_fees = 0.8,
income = total - transaction_fees
}
filter income > 1
group customer_id (
aggregate {
average total,
sum_income = sum income,
ct = count total,
}
)
sort {-sum_income}
take 10
join c=customers (==customer_id)
derive name = f"{c.last_name}, {c.first_name}"
select {
c.customer_id, name, sum_income
}
derive db_version = s"version()"
And the new plv8 extension allows you to write stored procedures in JavaScript within PostgreSQL — the richness of PostgreSQL’s procedural language support is truly amazing!

parquet_s3_fdw might seem like it just lets you access Parquet files on S3, but its significance is that PG can become a true lakehouse — essentially adding an analytics engine with unlimited storage capacity!
Built on top of it, pg_tier provides convenient tiered cold storage — you can easily archive rarely accessed massive cold data from PG to S3/MinIO using SQL!
If Parquet alone isn’t enough, ParadeDB’s pg_lakehouse takes this to a new level — you can now use PG directly as a lakehouse, reading Parquet, CSV, JSON, Avro, DeltaLake, and upcoming ORC format files from S3/MinIO/local filesystem for lakehouse analytics!
CREATE EXTENSION pg_lakehouse;
CREATE FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER s3_wrapper HANDLER s3_fdw_handler VALIDATOR s3_fdw_validator;
-- Provide S3 credentials
CREATE SERVER s3_server FOREIGN DATA WRAPPER s3_wrapper
OPTIONS (region 'us-east-1', allow_anonymous 'true');
-- Create foreign table
CREATE FOREIGN TABLE trips (
"VendorID" INT,
"tpep_pickup_datetime" TIMESTAMP,
"tpep_dropoff_datetime" TIMESTAMP,
"passenger_count" BIGINT,
"trip_distance" DOUBLE PRECISION,
...
)
SERVER s3_server
OPTIONS (path 's3://paradedb-benchmarks/yellow_tripdata_2024-01.parquet', extension 'parquet');
-- Query remote Parquet like a regular Postgres table
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM trips;
count
---------
2964624
ParadeDB’s pg_analytics and pg_search are also noteworthy — the former provides first-tier analytics performance, while the latter offers ElasticSearch BM25 full-text search capability as a PG alternative.
Tembo also provides four practical Rust PG extensions. Their pgmq provides a lightweight message queue API on PG, similar to AWS SQS and RSMQ, as an alternative to pgq.
In AI, pgvector 0.7 introduces major upgrades: sparse vectors (retiring pg_sparse!), half float quantization, doubled max vector dimensions to 4000, binary quantization (up to 64K dims), two new distance metrics and indexes. Most importantly, SIMD instructions are now supported — performance has improved dramatically compared to a year ago!
Plus other AI extensions: pg_vectorize helps wrap RAG services, pg_tiktoken counts OpenAI tokens in PG, pg_similarity provides 17 additional distance metrics, imgsmlr provides image similarity functions, bigm provides bigram-based full-text search, zhparser provides Chinese word segmentation.
For new data types: md5hash lets you efficiently store 128-bit MD5 digests natively. pg_idkit generates a dozen different ID schemes (UUIDv6, UUIDv7, nanoid, ksuid, ulid, etc.). rrule stores, parses, and processes calendar recurring events.
For database administration: pgdd accesses PG catalog via SQL, pg_later executes SQL asynchronously, pg_dirtyread reads dead tuples for data recovery, pg_show_plans shows running query execution plans!
For encryption: pg_tde provides experimental transparent encryption storage, pgsmcrypto provides Chinese SM cryptography (SM2,3,4) support.
Achieving Completeness#
Including previous extensions, Pigsty v2.7 has 255 PG extensions available across all operating systems. We can proudly say that no distribution or provider in the PostgreSQL ecosystem matches our extension count:
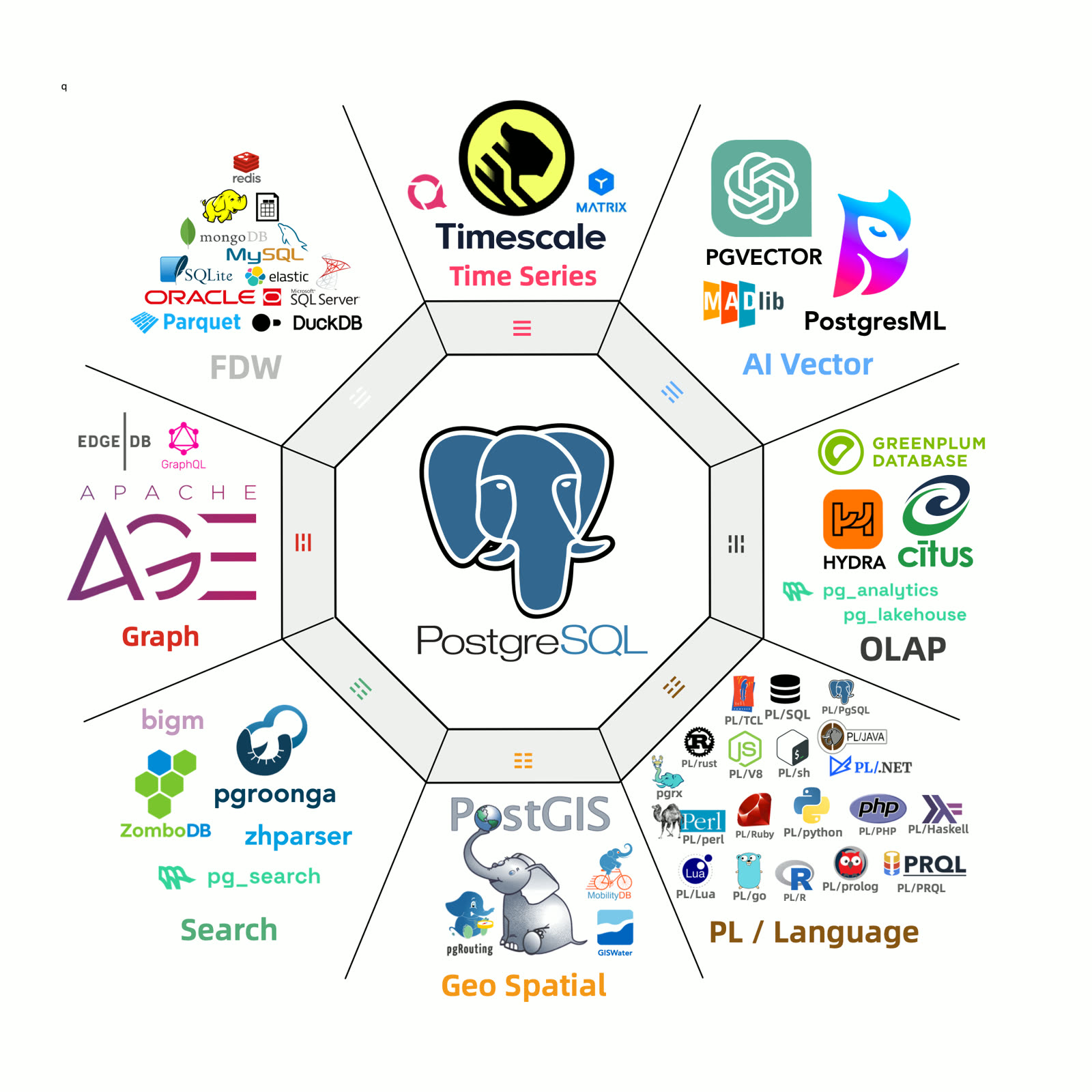
On EL systems, 230 RPM extensions are available (73 built-in + 157 third-party, 34 Pigsty-maintained). On Debian/Ubuntu, 189 DEB extensions are available (73 built-in + 116 third-party, 10 Pigsty-maintained).
Extensions are organized into 11 categories by function:
| Category | Extensions |
|---|---|
| TYPE | pg_uuidv7, pgmp, semver, timestamp9, uint, roaringbitmap, unit, prefix, md5hash, ip4r, asn1oid, pg_rrule, pg_rational, debversion, numeral, pgfaceting |
| GIS | pointcloud, pgrouting, h3, postgis, mobilitydb, geoip, h3_postgis, pointcloud_postgis |
| AI | pg_tiktoken, imgsmlr, svector, pg_similarity, pgml, vectorize, vector |
| OLAP | pg_lakehouse, duckdb_fdw, citus_columnar, parquet_s3_fdw, columnar, pg_analytics, timescaledb, pg_tier |
| FDW | hdfs_fdw, mysql_fdw, pgbouncer_fdw, mongo_fdw, sqlite_fdw, tds_fdw, ogr_fdw, oracle_fdw, multicorn, db2_fdw, wrappers |
These extensions can be combined for synergy, achieving 1+1 » 2 effects.
As TimescaleDB CEO Ajay stated in “Why PostgreSQL is the Foundation of Future Data,” PostgreSQL is becoming the de facto database standard.
Through the magic of extreme extensibility, PostgreSQL achieves completeness, balancing core stability with feature agility. A solid foundation plus amazing evolution speed makes it an anomaly in the database world, fundamentally changing the rules of the game.
Today, PostgreSQL is unstoppable. And Pigsty gives PostgreSQL wings to soar.
Out-of-the-Box ERP#
Similar to “domestic databases,” many domestic ERP software is awkwardly positioned because there’s already a good enough open-source ERP — Odoo (formerly OpenERP).
Many Pigsty users run PG for Odoo, which piqued my curiosity. After exploring the Odoo community and trying it myself, it’s incredibly powerful — wish I’d tried it earlier instead of fumbling with DIY solutions.
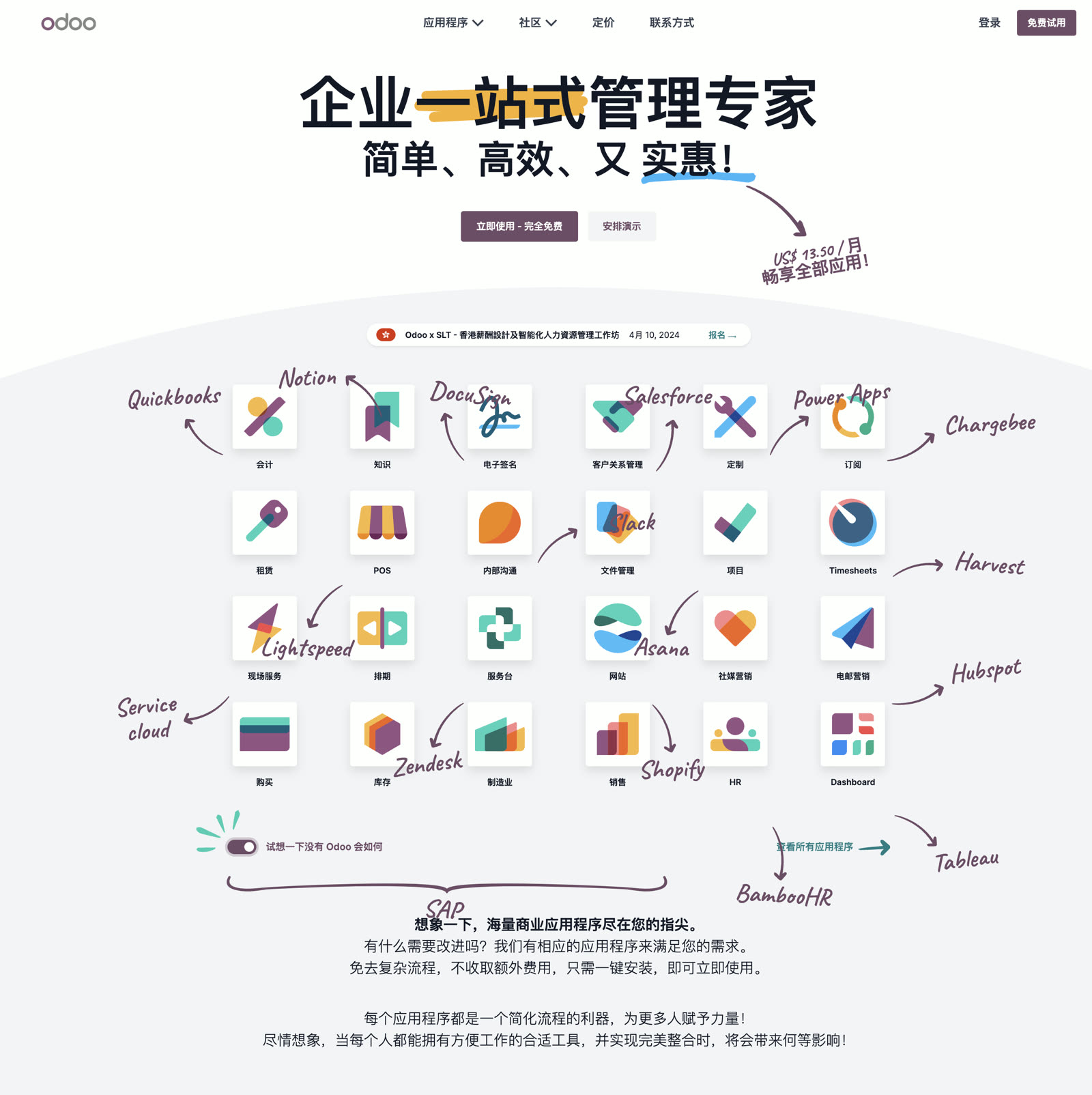
Odoo has many plugins with functionality far exceeding expectations — a true enterprise application suite king.
As open-source free software, Odoo monetizes via premium plugins, with reasonable subscription pricing. For those who want everything free, the community provides open-source alternatives for premium plugins!
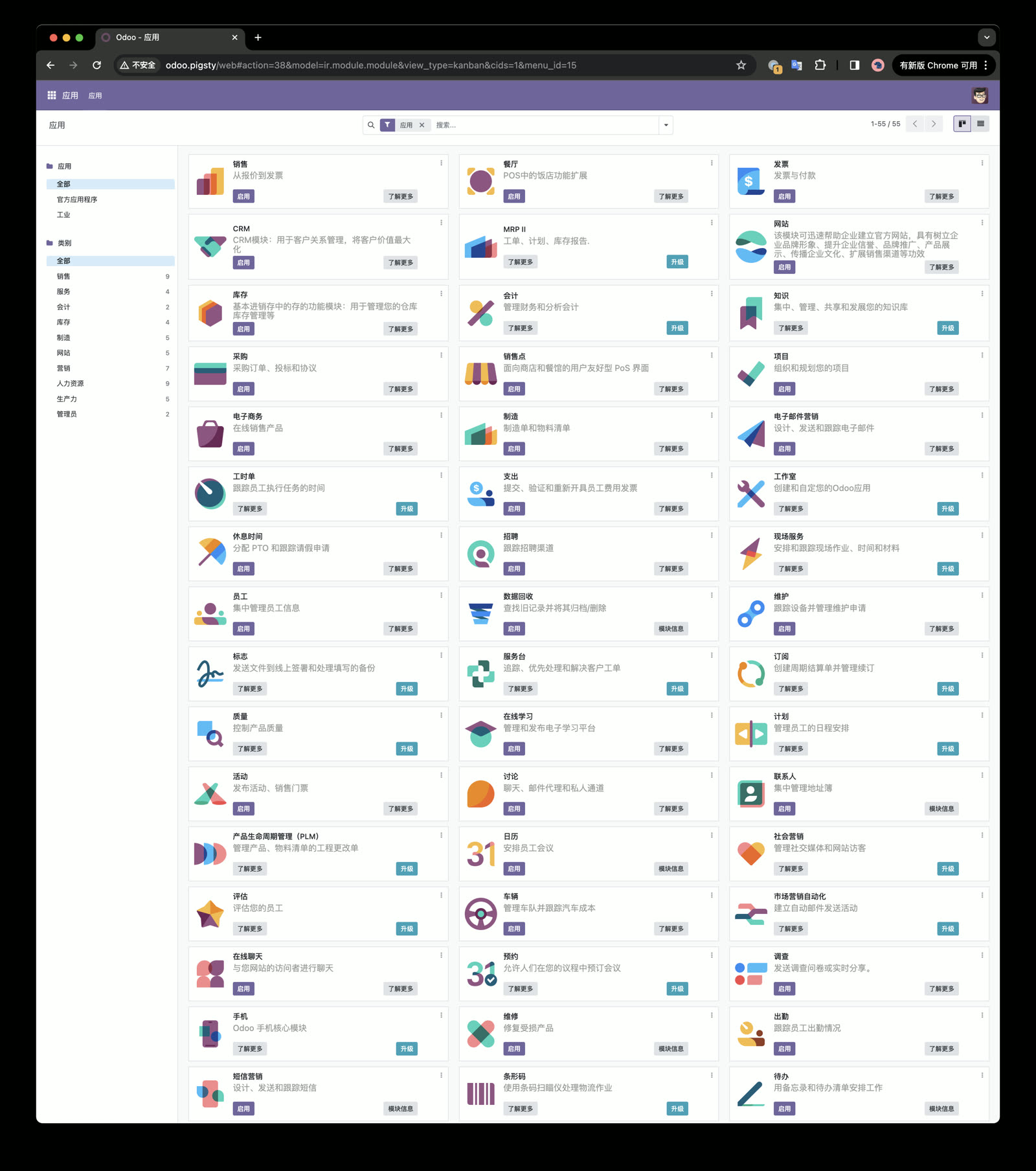
Odoo uses only PostgreSQL for data storage. The entire ERP suite needs just one PG database and one Docker image! A perfect PostgreSQL killer app example.
As a PostgreSQL distribution, there’s no reason not to support Odoo. Pigsty v2.7 provides a Docker Compose template for one-click Odoo deployment. You can reuse Pigsty’s infrastructure to easily expose web services via Nginx with HTTPS.
The result: on a bare VM, you can spin up a production-quality enterprise ERP with just a few commands!
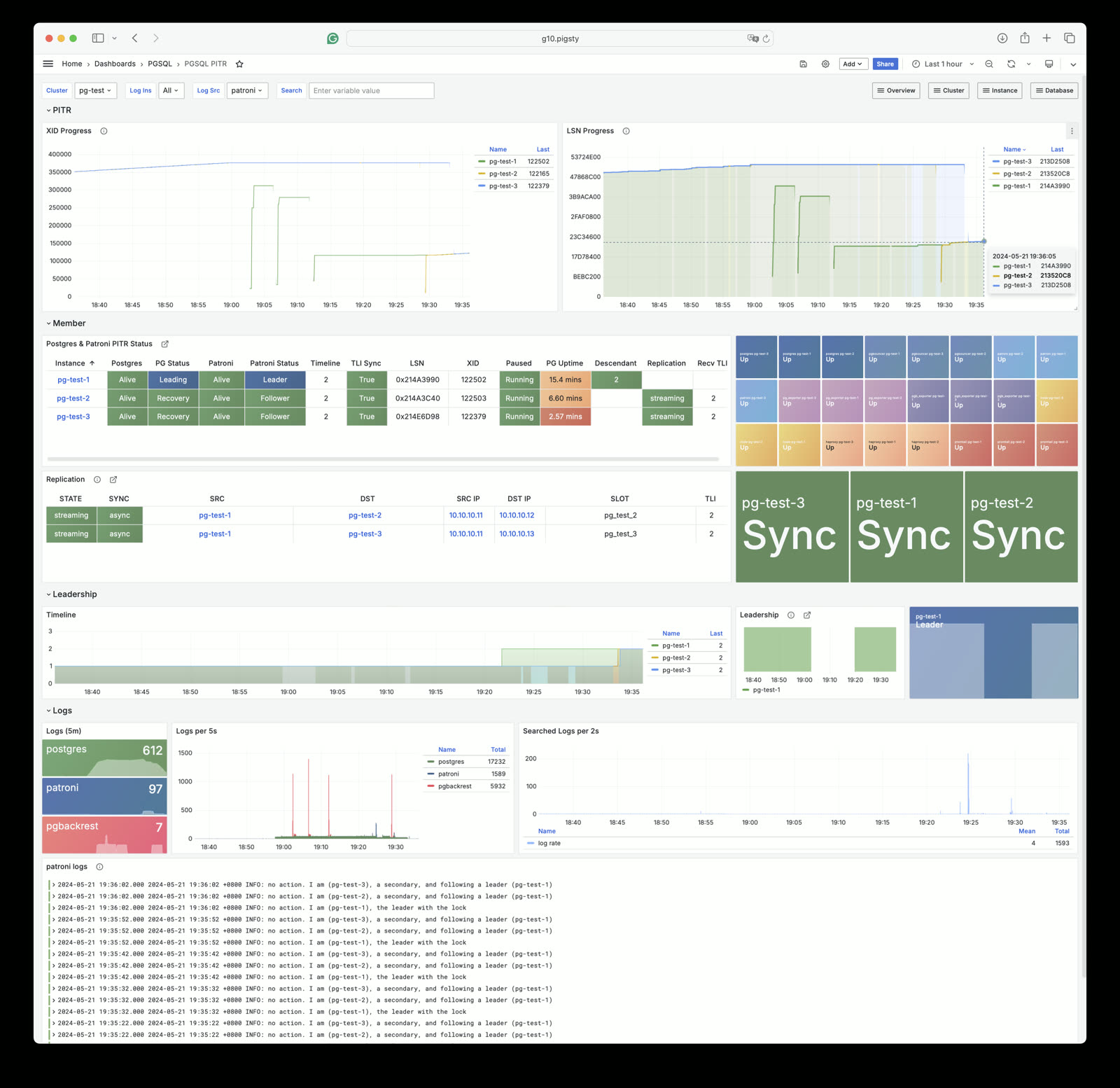
PITR and Dashboards#
ERP systems like Odoo have very different database requirements from traditional internet applications. I saw this in the Odoo community: “My Odoo has been running for years, now PostgreSQL has 2.5GB of data,” with replies: “That’s really big!”
2.5 GB is trivial for internet-scale apps but huge for ERP systems. Unlike performance and HA, ERP systems prioritize data integrity and confidentiality — often running on a single server without HA, needing only backup and Point-in-Time Recovery (PITR).
Pigsty already provides out-of-the-box PITR for rollback to any point in time. But the required information was scattered across the monitoring system, so Pigsty v2.7 provides a dedicated PGSQL PITR dashboard for PITR context.
Open Source vs Pro Edition#
In Pigsty v2.7, we’ve narrowed open-source OS support to Redhat, Debian, and Ubuntu mainlines. We provide first-class PostgreSQL 16 support on EL8, Debian12, and Ubuntu22.04 with offline packages. EL7, EL9, Debian11, and Ubuntu20.04 can still use Pigsty but won’t have offline packages — only online installation for initial deployment.
| Pigsty OSS | Pigsty Basic | Pigsty Pro | Pigsty Enterprise |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free! | 50,000 ¥/year | 150,000 ¥/year | 400,000 ¥/year |
| Self-sufficient veterans | Or 5,000 ¥/month | Or 15,000 ¥/month | Or 40,000 ¥/month |
| PG: 16 | PG: 15, 16 | PG: 12-16 | PG: 9.0-16 |
| OS: 3 main versions | OS: 5 latest versions | OS: All 5 versions | OS: Custom |
Pro differs mainly in compatibility and modules — PostgreSQL major versions, OS versions, and chip architectures.
In the original design, open source would include only INFRA, NODE, PGSQL, ETCD core modules. I debated whether to move MinIO, Redis, FerretDB (Mongo), and Docker to Pro, but ultimately kept them in open source — they’re already open, no reason to remove them. But future modules less related to PostgreSQL (Greenplum, MySQL, DuckDB, Kafka, Mongo, SealOS Cloud) will be Pro-only.
For compatibility, Pigsty Pro provides full lifecycle PG 12-16 support across seven major OS versions. We also maintain complete ARM64 Prometheus & Grafana repos for ARM servers and “domestic chips.”
Looking Forward#
Overall, Pigsty has reached my ideal state. Functionally, it’s already excellent! Exceeding RDS in some areas (like extension support and monitoring!).
But as they say, even fine wine fears a deep alley — so upcoming work will shift to operations, marketing, and sales. Sustainable open source requires user and customer support. If Pigsty has helped you, please consider sponsoring us or purchasing our subscriptions.
Speaking of marketing — next week (May 28), I’ll be in Vancouver for 2024 PostgreSQL Developer Conference, a.k.a. the first PGConf.Dev (formerly PG Con), discussing PostgreSQL’s future and pushing Pigsty to the global stage!
v2.7.0 Release Notes#
Highlights
New powerful extensions, especially Rust/pgrx-developed ones:
- pg_search v0.7.0: BM25 full-text search
- pg_lakehouse v0.7.0: Object storage/table format query engine
- pg_analytics v0.6.1: Accelerated analytics
- pg_graphql v1.5.4: GraphQL support
- pg_jsonschema v0.3.1: JSON Schema validation
- wrappers v0.3.1: Supabase FDW collection
- pgmq v1.5.2: Lightweight message queue
- pg_tier v0.0.3: S3 cold storage tiering
- pg_vectorize v0.15.0: RAG wrapper
- pg_later v0.1.0: Async SQL execution
- pg_idkit v0.2.3: UUID generation
- plprql v0.1.0: PRQL language
- pgsmcrypto v0.1.0: Chinese SM cryptography
- pg_tiktoken v0.0.1: OpenAI token counting
- pgdd v0.5.2: Catalog metadata via SQL
C/C++ extensions:
- parquet_s3_fdw 1.1.0: S3 Parquet lakehouse
- plv8 3.2.2: JavaScript stored procedures
- md5hash 1.0.1: Native MD5 hash type
- pg_tde 1.0-alpha: Experimental encryption
- pg_dirtyread 2.6: Read dead tuples
New Features
- Allow Pigsty to run in Docker VM images
- ARM64 packages for INFRA & PGSQL modules on Ubuntu and EL
- New installer script with Cloudflare download, version specification, better prompts
- PGSQL PITR dashboard for PITR observability
- Guardrails to prevent running playbooks on unmanaged nodes
- Per-distro config files: el7, el8, el9, debian11, debian12, ubuntu20, ubuntu22
Docker App Templates
- Odoo: Open-source ERP
- Jupyter: Jupyter Notebook container
- PolarDB: “Domestic database” for compliance
- Supabase: Updated to latest GA
- Bytebase: Using
latesttag - pg_exporter: Updated Docker examples
Software Upgrades
- PostgreSQL 16.3
- Patroni 3.3.0
- pgBackRest 2.51
- VIP-Manager v2.5.0
- HAProxy 2.9.7
- Grafana 10.4.2
- Prometheus 2.51
- Loki & Promtail: 3.0.0 (Warning: breaking changes!)
- Alertmanager 0.27.0
- BlackBox Exporter 0.25.0
- Node Exporter 1.8.0
- pgBackRest Exporter 0.17.0
- DuckDB 0.10.2
- etcd 3.5.13
- minio-20240510014138 / mcli-20240509170424
- pev2 v1.8.0 -> v1.11.0
- pgvector 0.6.1 -> 0.7.0
- pg_tle: v1.3.4 -> v1.4.0
- hydra: v1.1.1 -> v1.1.2
- duckdb_fdw: v1.1.0 recompiled for libduckdb 0.10.2
- pg_bm25 0.5.6 -> pg_search 0.7.0
- pg_analytics: 0.5.6 -> 0.6.1
- pg_graphql: 1.5.0 -> 1.5.4
- pg_net 0.8.0 -> 0.9.1
- pg_sparse (deprecated)
Bug Fixes
- Fixed variable whitespace in pg_exporters role
- Fixed
minio_clusternot commented in global config - Fixed EL7 template
postgis34should bepostgis33 - Fixed EL8
python3.11-cryptographydependency renamed topython3-cryptography - Fixed
/pg/bin/pg-rolenot getting OS username in non-interactive shell - Fixed
/pg/bin/pg-pitrnot prompting-X-Poptions correctly
API Changes
- New
node_write_etc_hostsparameter for controlling/etc/hostswrites - New
prometheus_sd_dirparameter for Prometheus static discovery directory - Configure script adds
-x|--proxyfor writing proxy info - Stopped parsing Nginx log detail labels in Promtail/Loki to avoid label cardinality explosion
- Using Alertmanager API v2 instead of v1
- Using
/pg/cert/ca.crtinstead of/etc/pki/ca.crtin PGSQL module
Offline Package Checksums
MD5 (pigsty-pkg-v2.7.0.el8.x86_64.tgz) = ec271a1d34b2b1360f78bfa635986c3a
MD5 (pigsty-pkg-v2.7.0.debian12.x86_64.tgz) = f3304bfd896b7e3234d81d8ff4b83577
MD5 (pigsty-pkg-v2.7.0.ubuntu22.x86_64.tgz) = 5b071c2a651e8d1e68fc02e7e922f2b3









