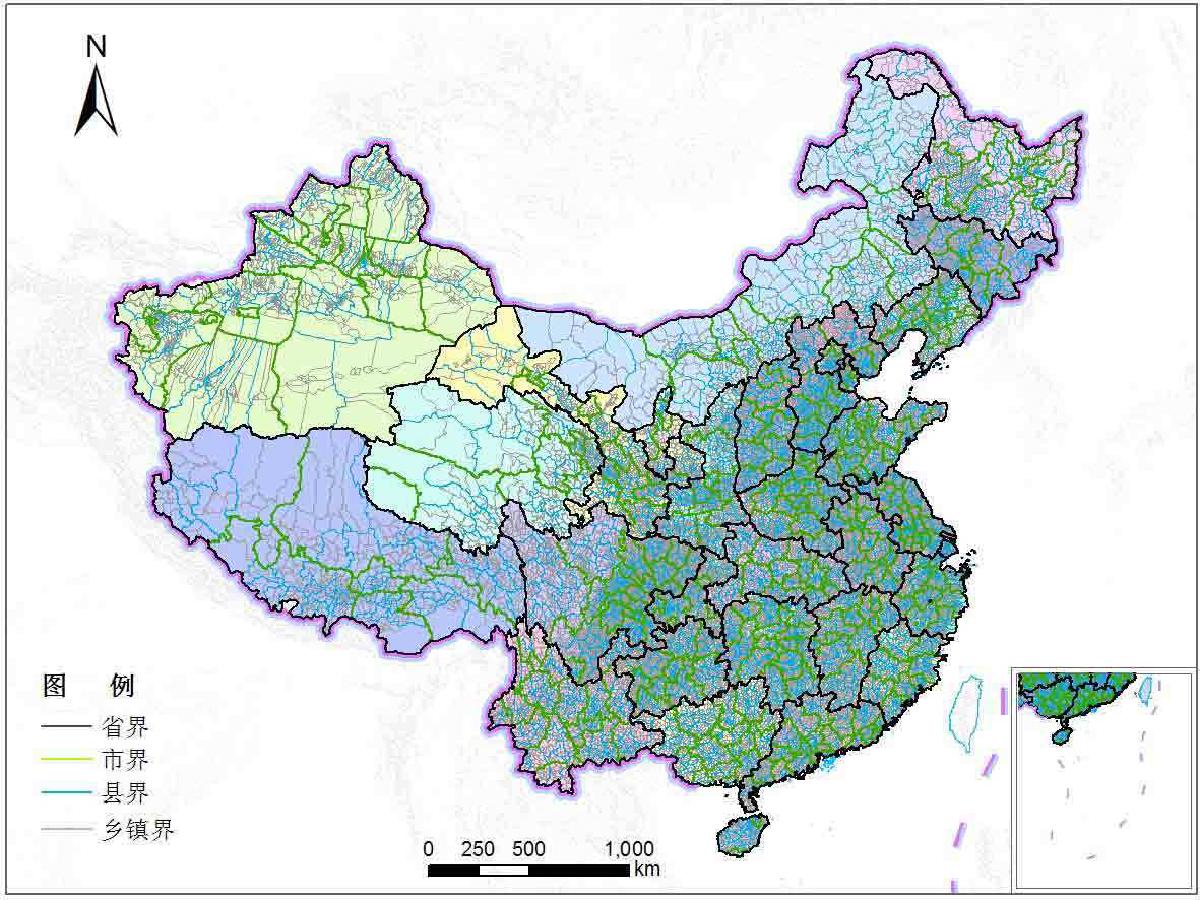
China’s administrative divisions are divided into several levels. The constitution stipulates three levels, but there are actually five levels: the four-tier system of “province—region—county (district)—township,” which becomes five tiers when including the central level.
Levels of Administrative Divisions#
China’s administrative divisions are divided into several government levels:
The constitution stipulates three levels (de jure level), but there are actually five levels (de facto level/practical level)
China’s current administrative hierarchy is the four-tier system of “province—region—county (district)—township,” which becomes five tiers when including the central level.
Due to China’s “party replacing government” issue, places with party committees can also be considered as one level of government. Therefore, village committees/neighborhood committees can also be seen as one level. When considering China’s administrative divisions, the central (national) level is generally not included.
Thus, there are five levels of administrative divisions: “province, city, county, township, village.” This is also the classification method used by the National Bureau of Statistics.
Number of Administrative Divisions#
Above provincial-level administrative regions, China can also be divided into 6 major regions, plus Hong Kong/Macao/Taiwan as two “major regions,” but these are not strict administrative divisions. The major regions are reflected in the first digit of the division code:
| Region Name | First Digit of Administrative Division Code |
|---|---|
| North China | 1 |
| Northeast China | 2 |
| East China | 3 |
| Central China | 4 |
| Southern China | 5 |
| Western China | 6 |
| Taiwan | 7 |
| Hong Kong/Macao | 8 |
- China has 34 provincial-level administrative units:
- 4 municipalities (centrally-administered municipalities)
- 23 provinces (including Taiwan)
- 5 autonomous regions
- 2 special administrative regions (SARs)
- Mainland China has 334 prefecture-level administrative units:
- 293 prefecture-level cities
- 8 prefectures
- 30 autonomous prefectures
- 3 leagues
- 2,851 county-level administrative units:
- 940 districts
- 363 county-level cities
- 1,377 counties
- 117 autonomous counties
- 49 banners
- 3 autonomous banners
- 1 special district
- 1 forestry area (total)
- 39,829 township-level administrative units:
- 8,016 subdistricts
- 20,654 towns
- 10,169 townships/sumu
- 990 ethnic townships/ethnic sumu
- 671,729 village-level administrative units:
- 99,935 neighborhood committees
- 571,794 village committees, including administrative villages and natural villages
- Total of 660 cities:
- 4 municipalities
- 293 prefecture-level cities
- 363 county-level cities
Additionally, there are special cases including sub-provincial cities, sub-prefecture-level cities, and sub-provincial districts (such as Shanghai’s Pudong and Tianjin’s Binhai).
Reference: Rules for Statistical Division Codes and Urban-Rural Classification Codes#
- Link: Rules for Statistical Division Codes and Urban-Rural Classification Codes
- Source: Department of Administration, National Bureau of Statistics
- Published: 2009-11-25 10:55
To standardize statistical division codes and urban-rural classification codes, and establish a unified “Statistical Division Code and Urban-Rural Classification Code Database” for various censuses, comprehensive statistics, sample surveys, and special surveys, these rules are formulated.
I. Structure of Statistical Division Codes and Urban-Rural Classification Codes#
Statistical division codes and urban-rural classification codes are divided into two segments of 17 digits, with the code structure as follows:
□ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ — □ □ □ □ □
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17- Statistical division code: first 12 digits
- Urban-rural classification code: last 5 digits
(I) Statistical Division Code#
The statistical division code consists of codes from positions 1-12, where each code represents:
- Positions 1-2: provincial code
- Positions 3-4: prefecture code
- Positions 5-6: county code
- Positions 7-9: township code
- Positions 10-12: village code
(II) Urban-Rural Classification Code#
The urban-rural classification code consists of codes from positions 13-17, where each code represents:
- Positions 13-14: urban-rural attribute code
- Positions 15-17: urban-rural classification code
II. Rules for Statistical Division Code Compilation#
(I) Coding Method for Administrative Division Codes Above County Level#
Administrative division codes above county level consist of codes from positions 1-6. In statistical work, statistical departments at all levels do not compile administrative division codes above county level, but uniformly adopt the national standard “Administrative Division Codes of the People’s Republic of China.”
(II) Coding Method for Division Codes Below County Level#
Division codes below county level consist of codes from positions 7-12, including township-level codes and village-level codes.
1. Township-Level Code Compilation Method#
Streets, towns, and townships confirmed by civil affairs departments are compiled according to the national standard “Coding Rules for Administrative Division Codes Below County Level” (GB/T 10114—2003), with township-level codes 001-399; development zones, mining areas, farms and similar township-level units not confirmed by civil affairs departments have township-level codes 400-599. Specific coding:
- 001-099: subdistricts
- 100-199: towns
- 200-399: townships
- 400-599: similar township-level units
2. Village-Level Code Compilation Method#
Village-level units confirmed by civil affairs departments have village-level codes 001-399; parks, mining areas, farms and similar village-level units not confirmed by civil affairs departments have village-level codes 400-599 (excluding 498, 598). Specific coding:
- 001-199: neighborhood committees
- 200-399: village committees
- 400-499: similar neighborhood committees (excluding code 498)
- 500-599: similar village committees (excluding code 598)
3. Special Case Coding Methods#
(1) Virtual Village-Level Units#
When village-level units are not established (or not specified) under township-level units, a virtual village-level unit is created under that township-level unit, with coding method:
Under subdistricts, towns and similar township-level development zones, technology parks, industrial parks, mining areas, university campuses, research institution parks, virtual village-level unit code is 498, named “XX Virtual Community”;
Under townships and similar township-level agricultural, forestry, animal husbandry, fishery farms and other agricultural activity areas, virtual village-level unit code is 598, named “XX Virtual Living Area.”
(2) County-Directly Administered Village-Level Units#
For village-level units directly administered by county-level units, the township-level code is uniformly coded as 198, and under code 198, village committees and neighborhood committees under its jurisdiction are further coded.
(3) Township-Directly Managed Village Groups#
Village groups directly managed by township-level units have village-level code 398.
(III) Requirements for Statistical Division Code Compilation#
- Basic length of statistical division codes is 12 digits; province, prefecture, county, township four-level codes are padded with zeros if less than 12 digits.
- Each code segment of division codes below county level is compiled in ascending order. When division codes are cancelled due to administrative changes, they are not reused.
- Township and village level units confirmed by civil affairs departments are coded in the 001-399 range, with names uniformly adopting official names confirmed by civil affairs departments.
- Similar township-level units are township-level units not confirmed by civil affairs departments, with names filled according to actual names.
- Similar neighborhood committees and similar village committees are village-level units not confirmed by civil affairs departments. If actual names do not contain words like neighborhood committee, village committee, family committee, production team, company, team, management area, pastoral committee, gacha, then “community” is added after the actual name of similar neighborhood committees; “living area” is added after the actual name of similar village committees.
- Division names in statistical division codes use standard Chinese characters, Chinese numerals (such as one, two, three, etc.) and full-width parentheses for writing. Other letters, numbers, punctuation, characters and spaces are incorrect. Chinese characters must not use traditional characters; simplified characters should be written according to the simplified character table promulgated by the state.
III. Urban-Rural Classification Code Compilation Rules#
(I) Urban-Rural Attribute Code Compilation Method#
The urban-rural attribute code consists of codes from positions 13-14. Where: position 13 represents township-level attributes, position 14 represents village-level attributes.
1. Urban-Rural Attribute Code Compilation Principles#
- (1) Urban-rural attribute codes are compiled at township and village level units.
- (2) For township-level units, position 13 is compiled according to township-level attribute coding method, position 14 is coded as 0.
- (3) For village-level units, position 13 is the township-level attribute code of the township-level unit it belongs to, position 14 is compiled according to village-level attribute coding method.
2. Township-Level Attribute Coding Method#
Township-level attribute codes represent township-level attributes of subdistricts, towns, townships and similar township-level units. Township-level attribute codes use digits 1-3:
- 1 represents: county government seat
- 2 represents: connected township-level area
- 3 represents: other township-level areas
3. Village-Level Attribute Coding Method#
Village-level attribute codes represent village-level attributes of neighborhood committees (communities), village committees and similar village-level units. Village-level attribute codes use digits 1-9:
- 1 represents: township government seat
- 2 represents: completely connected village-level area
- 3 represents: partially connected village-level area
- 4 represents: village-level area completely connected to other districts/cities
- 5 represents: village-level area partially connected to other districts/cities
- 6 represents: village-level area completely connected to other towns
- 7 represents: village-level area partially connected to other towns
- 8 represents: special areas
- 9 represents: other village-level areas
For related explanations of township-level and village-level attributes, see “Urban-Rural Classification Implementation Measures.”
4. Notes on Urban-Rural Attribute Codes#
(1) Special Areas#
In urban-rural attribute codes, special areas only refer to the following two situations:
- In similar neighborhood committees, residential living areas of development zones, mining areas, colleges and universities, scientific research units, etc. with permanent population reaching or exceeding 3,000 people.
- In similar village committees, agricultural, forestry, animal husbandry, fishery farms and other areas mainly engaged in agricultural activities with permanent population reaching or exceeding 3,000 people and non-agricultural industry employees reaching 70%.
When similar neighborhood committees and similar village committees do not meet the above requirements and also do not meet coding requirements 1-7, village-level attribute is uniformly coded as 9.
(2) Agricultural, Forestry, Animal Husbandry, Fishery Farms#
The village-level attribute code for headquarters of agricultural, forestry, animal husbandry, fishery farms is uniformly coded as 1. Subordinate production units connected to headquarters have village-level attribute codes 2 or 3. Subordinate production units not connected to headquarters have village-level attribute code 9. When permanent population reaches 3,000 and non-agricultural industry employees reach 70%, unconnected subordinate production units have village-level attribute code 8.
(3) Village-Level Attributes with Only One Village-Level Unit#
For township-level units with only one village-level unit, whether actually existing or virtual, the corresponding village-level attribute code is uniformly coded as 1.
(4) Unconnected Neighborhood Committees#
When neighborhood committees are not connected to government seats, if there is agricultural land, village-level attribute code is 9; if there is no agricultural land (or no clear area), village-level attribute code is 8.
(II) Urban-Rural Classification Code Compilation Method#
1. Urban-Rural Classification Code Structure#
Urban-rural classification codes consist of codes from positions 15-17. Position 15 as “1” represents urban; position 15 as “2” represents rural. Specific coding:
- 111 represents: main urban area
- 112 represents: urban-rural transition area
- 121 represents: town center area
- 122 represents: town-rural transition area
- 123 represents: special areas
- 210 represents: township center area
- 220 represents: villages
2. Urban-Rural Classification Code Compilation Principles#
When dividing urban and rural areas, local statistical departments do not directly compile urban-rural classification codes, but generate urban-rural classification codes through conversion of statistical division codes and urban-rural attribute codes.
Appendix: Park and Government-Enterprise Integration Unit Code Compilation Method#
To meet the needs of various localities for summarizing and classifying parks and government-enterprise integration units, the following park and government-enterprise integration unit code compilation method is proposed for reference.
I. Code Structure#
Park and government-enterprise integration unit codes are 4-digit codes, compiled corresponding to statistical division codes. Structure:
1 2 3 4
□ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ …… □ □ □ □
Statistical division code Park and government-enterprise integration unit codePark and government-enterprise integration unit codes are divided into three segments:
- First segment is position 1, representing categories of parks and government-enterprise integration units: development zones, processing bonded zones, industrial parks, technology parks, trade and logistics parks, agricultural demonstration zones, agricultural/forestry/animal husbandry/fishery farm areas, other areas;
- Second segment is position 2, representing approval levels of parks and government-enterprise integration units: national, provincial, prefecture/city, county, others;
- Third segment is positions 3-4, representing sequence codes for parks and government-enterprise integration units of the same area, same category, same level.
II. Coding Principles#
When compiling statistical division codes, any area actually containing parks or government-enterprise integration units can compile park and government-enterprise integration unit codes.
Park and government-enterprise integration unit category coding method:
- 1 represents: development zones
- 2 represents: processing bonded zones
- 3 represents: industrial parks
- 4 represents: technology parks
- 5 represents: trade and logistics parks
- 6 represents: agricultural demonstration zones
- 7 represents: agricultural/forestry/animal husbandry/fishery farm areas
- 8 represents: other areas
Park and government-enterprise integration unit level coding method:
- 1 represents: national level
- 2 represents: provincial level
- 3 represents: prefecture/city level
- 4 represents: county level
- 5 represents: others
Park and government-enterprise integration unit sequence codes are compiled in ascending order 01-99 under the same area, same category, same level.
III. Notes on Park and Government-Enterprise Integration Unit Coding#
- Development zones refer to economic and technological development zones and high-tech development zones approved by people’s governments at all levels.
- Processing bonded zones refer to various processing zones and bonded zones approved by people’s governments at all levels.
- Industrial parks refer to industrial parks and mining areas mainly engaged in industrial production approved by people’s governments at all levels.
- Technology parks refer to technology demonstration zones, technology zones, technical-industrial-trade parks approved by people’s governments at all levels, excluding high-tech development zones.
- Trade and logistics parks refer to parks mainly engaged in commodity trading, logistics, ports, warehousing approved by people’s governments at all levels, excluding bonded zones and processing zones.
- Agricultural demonstration zones refer to various demonstration zones mainly engaged in agricultural production activities approved by people’s governments at all levels.
- Agricultural/forestry/animal husbandry/fishery farms refer to farms, forests, ranches, fisheries approved by governments at all levels (or government competent departments), including areas such as groups, farms, teams, management areas under production and construction corps and land reclamation bureaus.
- Other areas refer to areas of parks and government-enterprise integration units other than those mentioned above.
- National, provincial, prefecture/city, county, others refer to the following approval levels:
- National level: established by State Council or relevant departments under State Council;
- Provincial level: established by provincial people’s governments;
- Prefecture/city level: established by prefecture-level city people’s governments, prefectural administrative offices;
- County level: established by county, county-level city people’s governments;
- Others: established by people’s governments or dispatched agencies other than those mentioned above.